retroactive capital gains tax history
Understanding The Proposed Retroactive Capital. Since the early 1950s the long-term capital gains rate has been lower than the top ordinary income tax rate.

Why Won T Canada Increase Taxes On Capital Gains Of The Wealthiest Families Fon Commentaries Vol 2 No 20 Finances Of The Nation
Indeed we need not look back too far in history to find.

. And 2 the period of retroactivity is not excessive. The 20 tax rate on capital gains can raise as high as 318 for some individuals. These changes would relate back to April 28 or May 28 2021.
In 1969 during Richard Nixons administration Congress passed the Tax Reform Act of 1969 which raised certain income tax rates with at least twenty retroactive effective dates. But prior to such legislative change could be subject to a higher capital gains rate. One idea in play is a retroactive capital gains tax increase raising the top tax rate currently 238 percent imposed on the gain from the sale of assets held longer than a year9 President Bidens budget proposal suggested raising the rate on such capital gains to 434 percent for households with income over 1 million effective for all sales on or after April 2021.
President Biden has been clear that he wants to raise taxes on capital gains for high earners. This change is significant because it would be the first retroactive capital gains increase in US federal tax history. More specifically in August of 1993 Congress passed the Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act.
For taxpayers with income of over 1 million long-term capital gains will be taxed at ordinary rates. When taxes go up investors naturally rush to realize their gains at the lower tax bracket before the hike takes effect. A historical review suggests that any tax legislation enacted in 2021 could have retroactive effect to transactions.
Under the Jobs and Growth Tax Relief Reconciliation Act. CNBCs Robert Frank reports. Under the rules then in effect they had to pay tax on only half that amount.
If the capital-gains rate is increased millionaire and billionaire taxpayers would actually face a 434 tax on capital asset sales when factoring in a 38 tax linked to the Affordable Care Act. History Set forth on page 62 of the Green Book tax is the proposal we have all heard about the increase in the capital gains tax rate that will raise the top rate for households earning more than 1 million to 434 a number that includes an existing 38 surtax to help pay for the Affordable Care Act from the current 238. But until a Wall Street Journal scoop published Thursday night it wasnt known that he wants those taxes raised retroactively.
In the Tax Reform Act of 1986 enacted October 22 1986 the tax rate on long-term capital gains was increased from 20 in 1986 to 28 in 1987. But as its Treasury Report makes clear it fears that the steep capital-gains rate increase. There is pressure for another wealth tax on individuals making 5 million or more who would see another 3 tax raise.
Completed at any time in 2021. Retroactive Changes to Long-Term Capital Gains. The Green Books proposed change to long-term capital gains is retroactive.
In 2003 this was further reduced to 15. A report by the Tax Policy Center shows that capital gains realizations rose by 60 percent in 1986 before the new tax rate of 28 percent was due to come into effect in 1987 from the previous 20 percent. Retroactive tax provisions in 1969 1987 and 1993 withstood constitutional challenges in part because they were designed to create more taxpayer equity and to eliminate loopholes.
If the capital-gains rate is increased millionaire and billionaire taxpayers would actually face a 434 tax on capital asset sales when factoring in a 38 tax linked to the Affordable Care Act. Indeed we need not look back too far in history to find a prime example of retroactive tax increases. The Court reasoned that Congress meant to correct a mistake that afforded an unjustified tax loophole and applied the revision retroactively for a modest period.
While the most significant recent capital gains rate change provided by the JGTRRA was largely. Made permanent the capital gains rate changes in the JGTRRA but provided for a maximum rate of 20 percent. History Of The Capital Gains Tax.
The 1987 capital gains tax collections were. The reason for retroactivity is that there is a long history of taxpayers accelerating capital gains before tax increases take effect. One idea in play is a retroactive capital gains tax increase raising the top tax rate currently 238 percent imposed on the gain from the sale of assets held longer than a year9.
Similarly widespread exits jumped 40 percent. In recent years such retroactive rate changes have occurred as late into the year. Then in October President Gerald Ford signed the Tax Reform Act.
The test upholds retroactive tax application if. In 1997 the top rate was reduced from 28 to 20. And so the Biden administration proposes to increase the capital-gains top rate from 238 percent to 434 percent to pay for its 6 trillion American Families Plan which includes about 18 trillion for child care education and paid employee leave.
This resulted in a 60 increase in the capital gains tax collected in 1986. Effective for taxable years beginning after 31 December 2012 ie. 1st Retroactive Capital Gains Increase in US.
President Joe Biden is formally calling for his proposal for the largest capital gains tax in history to be retroactive. 1 the legislation has a rational legislative purpose and is not arbitrary. This isnt a judgment on the merits or demerits of raising top capital gains rates either to Bidens preferred 396.
There have been two major increases in the tax rate applicable to long-term capital gains in the past 50 years. Signed 2 January 2013.

Good And Bad News From The Aba Futures Report Perspective Decade Century Aba Bad News

Cryptocurrency Tax War Part Ii

Tax Policy Reforms 2020 Oecd And Selected Partner Economies Oecd Ilibrary
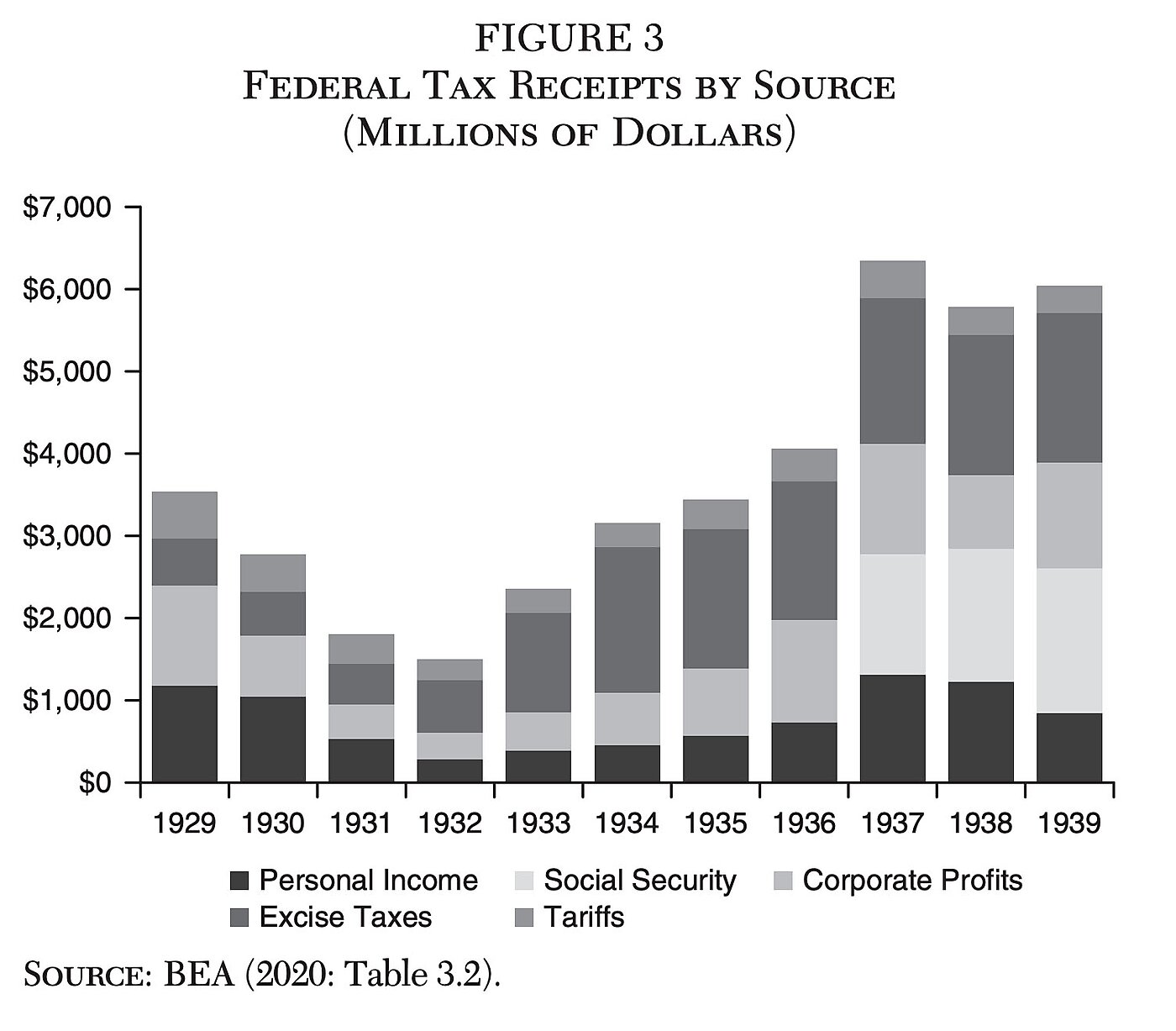
The Economic Impact Of Tax Changes 1920 1939 Cato Institute

Tax Policy Reforms 2020 Oecd And Selected Partner Economies Oecd Ilibrary

Tax Policy Reforms 2020 Oecd And Selected Partner Economies Oecd Ilibrary

Macroeconomic Effects Of The Anticipation And Implementation Of Tax Changes In Germany Evidence From A Narrative Account Christofzik 2022 Economica Wiley Online Library

How To Help Your Real Estate Investor Clients Structure Their Businesses Accounting Today In 2021 Real Estate Investor Real Estate Investors

Tax Policy Reforms 2020 Oecd And Selected Partner Economies Oecd Ilibrary

Tax Increases Are Coming Or Are They Bny Mellon Wealth Management

Macroeconomic Effects Of Tax Rate And Base Changes Evidence From Fiscal Consolidations In Imf Working Papers Volume 2018 Issue 220 2018

Macroeconomic Effects Of Tax Rate And Base Changes Evidence From Fiscal Consolidations In Imf Working Papers Volume 2018 Issue 220 2018

Tax Policy Reforms 2020 Oecd And Selected Partner Economies Oecd Ilibrary

Tax Policy Reforms 2020 Oecd And Selected Partner Economies Oecd Ilibrary
Proposed Impactful Tax Law Changes And What You Can Do Now Johnson Pope Bokor Ruppel Burns Llp

Managing Tax Rate Uncertainty Russell Investments

Retroactive Effective Date For Capital Gains Tax Increase Is A Bad Idea
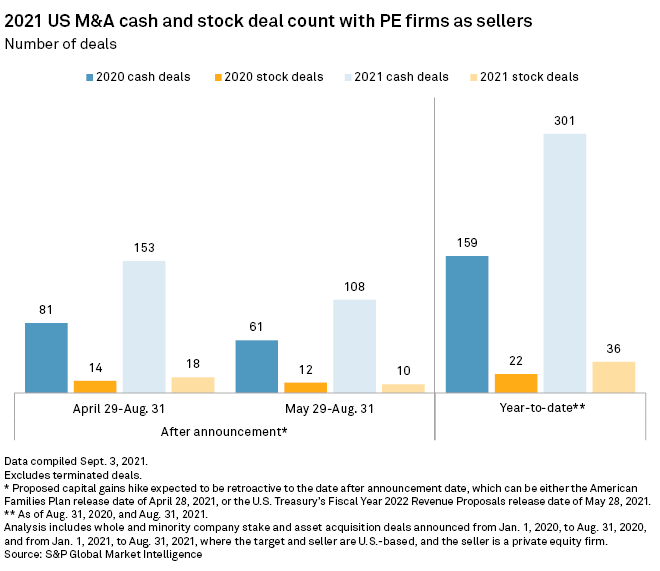
Higher Us Capital Gains Tax Proposal Spurs Pe M A Rush S P Global Market Intelligence
